Hemp

HEMP
Crop Profile
Get Involved!
What is hemp?
Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) is a versatile crop that can be used for its stalk (bast fiber and/or hurd), seed (grain or oil), or flower (bud or oil); it is commonly said that there are over 25,000 products that hemp is used in today. Considered one of the oldest crops in cultivation, hemp was once widely grown as a commodity fiber crop in the United States from the mid-18th century until its decline in the 20th century, brought upon by shrinking demand and government regulations aimed at marijuana (drug-type cannabis). Restrictions led to its eventual ban in 1970 with the passage of the Controlled Substances Act. Shifts in public opinion regarding cannabis and grassroots lobbying led to the legalization of permitted research beginning with the 2014 Farm Bill. Passage of the 2018 Farm Bill subsequently removed hemp from the list of controlled substances and legalized commercial production of hemp in the US, opening the door for re-development of a domestic hemp industry. Wisconsin responded swiftly by launching a pilot hemp program in 2018 until January 2022, when it relinquished authority over to the USDA.
What is the difference between hemp and drug-type cannabis?
Hemp and drug-type cannabis (commonly called “marijuana”) are different types of plants within C. sativa that are distinguished by their chemical composition. Hemp is legally defined as cannabis containing not more than 0.3% THC, the psychoactive compound found in C. sativa. Conversely, if the THC level is greater than 0.3%, the plant is classified as drug-type cannabis. Drug-type cannabis plants have been bred to produce a high amount of THC in the range of 10 to 30 percent.
What is hemp grown for?
Hemp is grown as a food and fiber crop and harvested for its seeds (grain), stalk (bast fiber and hurd) and flower.
- Hemp seeds (grain) can be processed into hemp hearts and used in a variety of food products such as granola and hemp milk. Hempseed oil extracted from the seeds are used in cooking oil, dietary supplements, personal hygiene products, paints, solvents, lubricants, and medicinal and pharmaceutical products.
- Hemp stalks are harvested for their fibers, which are used to manufacture hundreds of products, including rope, paper, construction materials, carpeting, textiles, insulation, animal bedding and bioplastics. There are two main types of fibers within the plant, the bast and the hurd, and each has different qualities and uses.
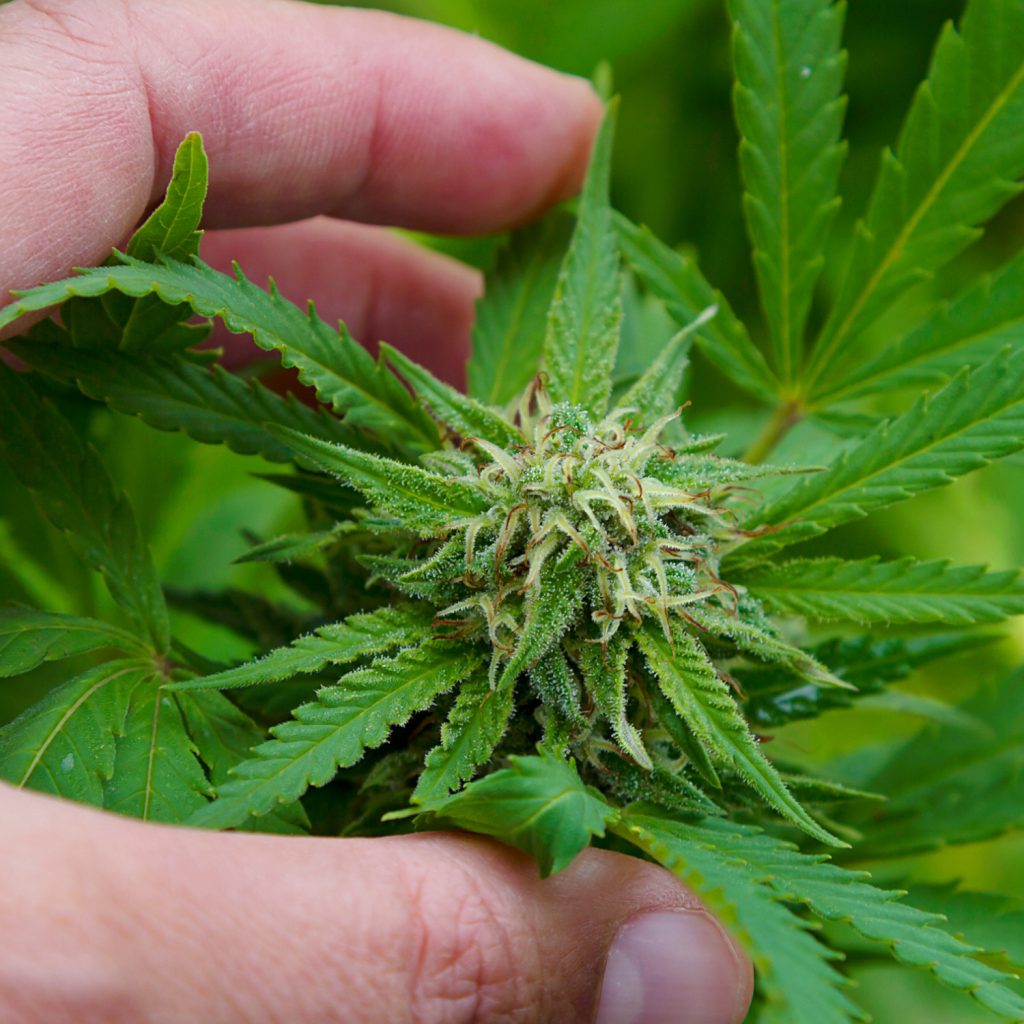
- Hemp flower is harvested for smoking and the extraction of cannabinoids, especially CBD. Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in the resins of C. sativa flowers. Over one hundred cannabinoids have been identified to date and they have shown some promise in helping treat certain health conditions such as epilepsy and anxiety.
How is hemp grown?
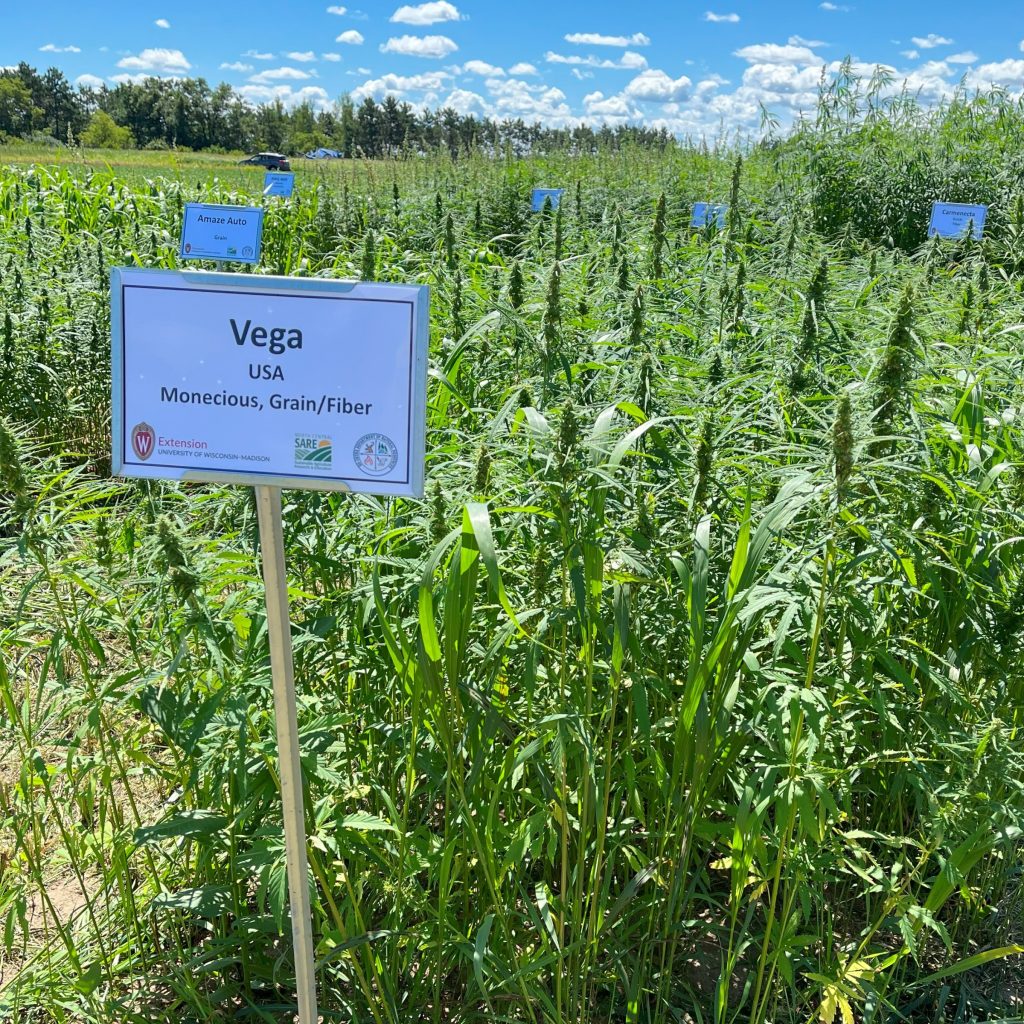
Production practices for hemp differ based on intended use. Hemp for grain and fiber production is typically grown on a large scale using conventional farm equipment such as a grain drill, mower, combine, and baler. Seed is harvested using a grain combine while stalks for fiber are cut and baled using haying equipment. Stalks must go through a process called retting between cutting and baling to help separate the bast from the hurd fibers. Hemp may be grown as a dual-purpose crop for grain and fiber.
Hemp grown for cannabinoid production is much more labor intensive and akin to specialty/vegetable crop production. Plants are usually started from feminized seed and transplanted into rows of black plastic lined with drip irrigation. Plants are spaced much further apart, with recommendations ranging from 1 foot on-center up to 6 feet on-centers. At harvest time, plants are cut by hand at the base (a machete is usually the tool of choice) and hung up to dry in a barn until further processing/extraction may take place.
For more detailed information on hemp production, see the Resources and Information section below.
Research Status and Priorities
Markets
Plant Material
Rules and Regulations
Grant Opportunities for Producers
Opportunities for Engagement
Do you grow, process, or sell hemp or hemp products? If so, we need your help! UW-Madison offers many opportunities to get involved in the research and development of a hemp industry in the Upper Midwest. We are looking for collaborators on the following initiatives.



Aware of any feral/wild hemp locations and interested in being compensated for your knowledge? Interested in contributing to a larger hemp genetics and breeding research effort? Contact Dr. Ademola Aina for more information.
Experienced row crop producer interested in being compensated for your skills/knowledge? Looking to work on the cutting edge and conduct participatory on-farm trials of grain/fiber hemp with costs of seed and cannabinoid testing covered? Contact Phillip Alberti for more information or apply here.
Interested in receiving significantly discounted cannabinoid testing costs in exchange for data sharing? Interested in contributing to the largest public hemp database in the Midwest which has been utilized to inform positive policy change at the federal level? Visit the Midwestern Hemp Database (Grain and Fiber, High CBD) or contact Phillip Alberti for more information.
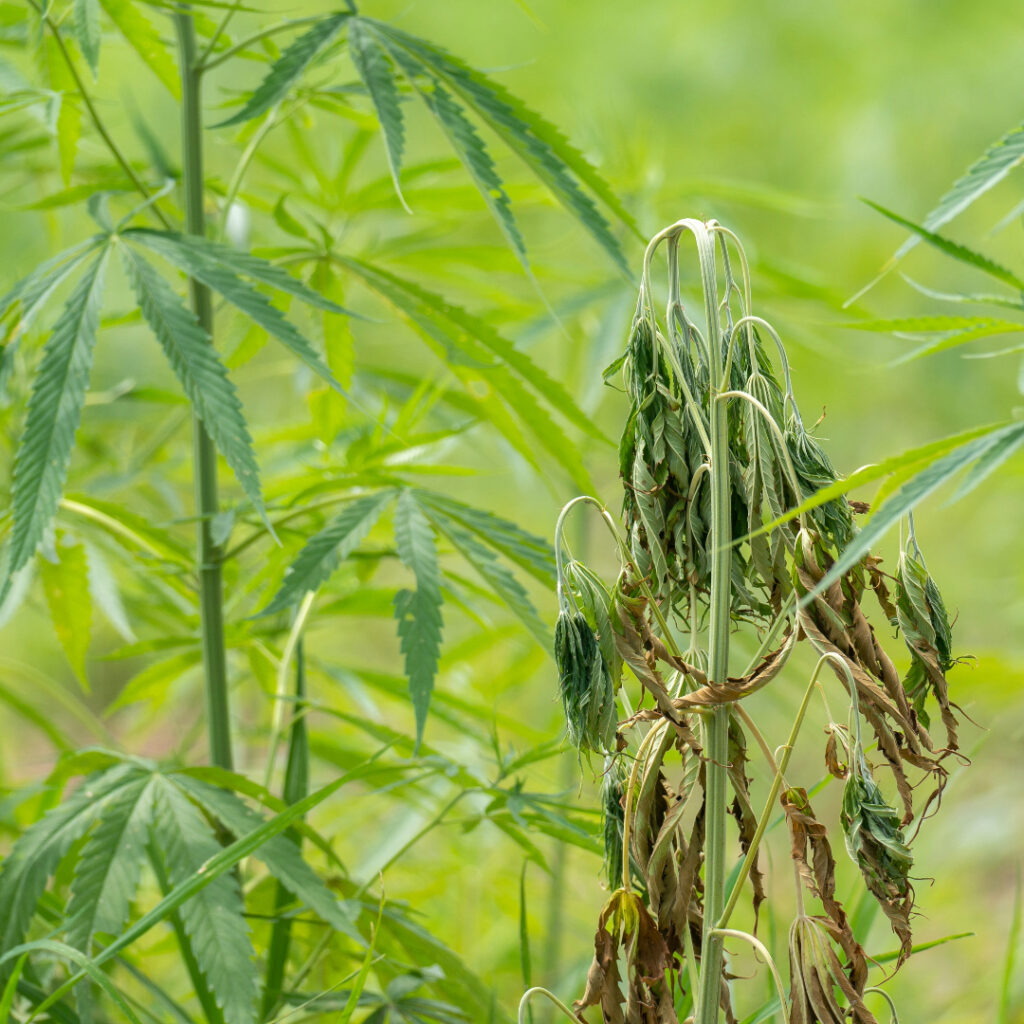
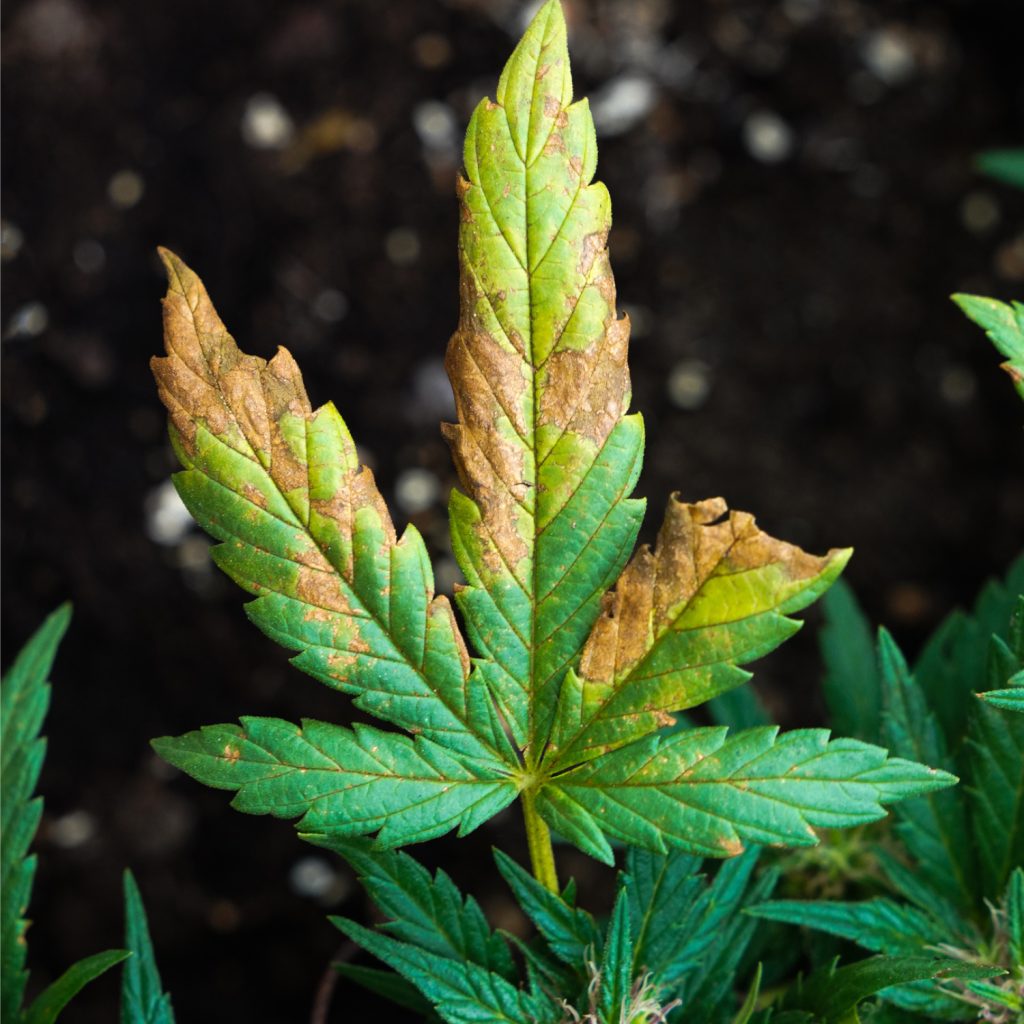



Are you a hemp grower with experience managing pest and disease issues? The Ellison lab invites you to take a survey to share information on the pest populations you manipulate, management strategies you use, and how these strategies may affect those populations. The first 50 respondents will be entered in a drawing to win a $10 Kwik Trip gift card. Take the survey here. For questions, contact Cheyanne Mattie.
Having hemp disease issues in your field? In the Ellison group, we aim to survey hemp fields and diagnose crop diseases to determine which plant pathogens are currently in hemp fields across Wisconsin. Interested in learning more about plant disease diagnostic services? Contact Dr. Derrick Grunwald for more information.
Experienced hemp grower? Looking to conduct participatory on-farm trials of high cannabinoid hemp with costs of seed and cannabinoid testing covered? Interested in networking with other growers while helping to develop compliant harvest schedules for high cannabinoid hemp cultivars? Consider getting involved in the Cultivar Check Program! Contact Phillip Alberti for more information or apply here.
Resources and information
Read
Watch
These videos cover a range of topics including hemp for fiber, grain, and CBD production. More videos can be found on the the Wisconsin Hemp YouTube Channel. Also check out the Wisconsin Hemp by Hand Webinar Series for interviews with hemp industry leaders and real world applications of hemp.
UW-Madison Hemp Research Updates
Bryan Parr (Legacy Hemp)
Dr. Shelby Ellison (University of Wisconsin-Madison) and Leah Sandler (Michael Fields Agricultural Institute)
Leah Sandler (Michael Fields Agricultural Institute)
Dr. Shelby Ellison and Dr. Rodrigo Werle (University of Wisconsin-Madison)
University of Wisconsin-Madison Extension and Sunny Skies CBD
Listen
Resources for Tribal Communities
Canndigenous
Hempstead Project Heart
Indigenous Cannabis Coalition
Indigenous Hemp Conference
Marijuana Legalization in Indian Country: Selected Resources (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
More Resources
Colorado State University
Cornell Hemp
Kentucky State University
Michael Fields Agricultural Institute
Oregon State University
– Industrial Hemp Stakeholder Database
Purdue University
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champagne
University of Kentucky
University of Vermont
University of Wisconsin-Madison Hemp Compass (financial planning tool)