
Image 1: Dan Brick, Brickstead Dairy, LLC, demonstrating the importance of cover crops to a group of elected officials and community leaders. This field was planted with a diverse mix of cover crops including radishes and sunflowers.
Cover crops provide a wide range of benefits including, improved soil infiltration, reduced erosion, increased soil organic matter, enhanced soil biology, and improved habitat for wildlife. The Fox Demo Farms Network is working with our producers to identify the realized benefits and the feasibility of having permanent soil cover of in northeast Wisconsin (Image 1).
Cover Crops:
- Permanent soil cover is defined as having year-round cover either in the form of residue mulch, which is naturally decomposed by microbes in the soil, or cover crops, which are either interseeded or planted late in the season.
Benefits of Cover Crops
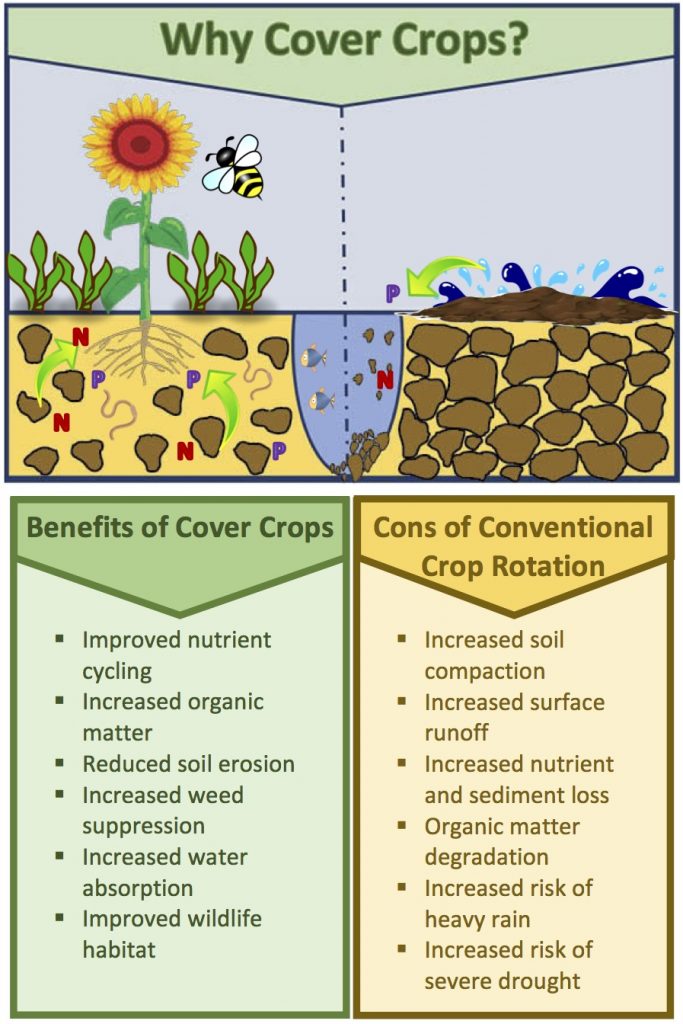
Figure 1: Graphic by Fox Demo Farms. Illustrates the benefits of cover crops and the cons of conventional crop rotation.
Check out this video demonstrating what cover crops can do for soil health and water quality.
Two fields at Wiese Brothers Farms, one with cover crops and one without…notice the difference in surface water clarity. Cover crops help keep sediment on the field and working for you, rather than in our waterways.
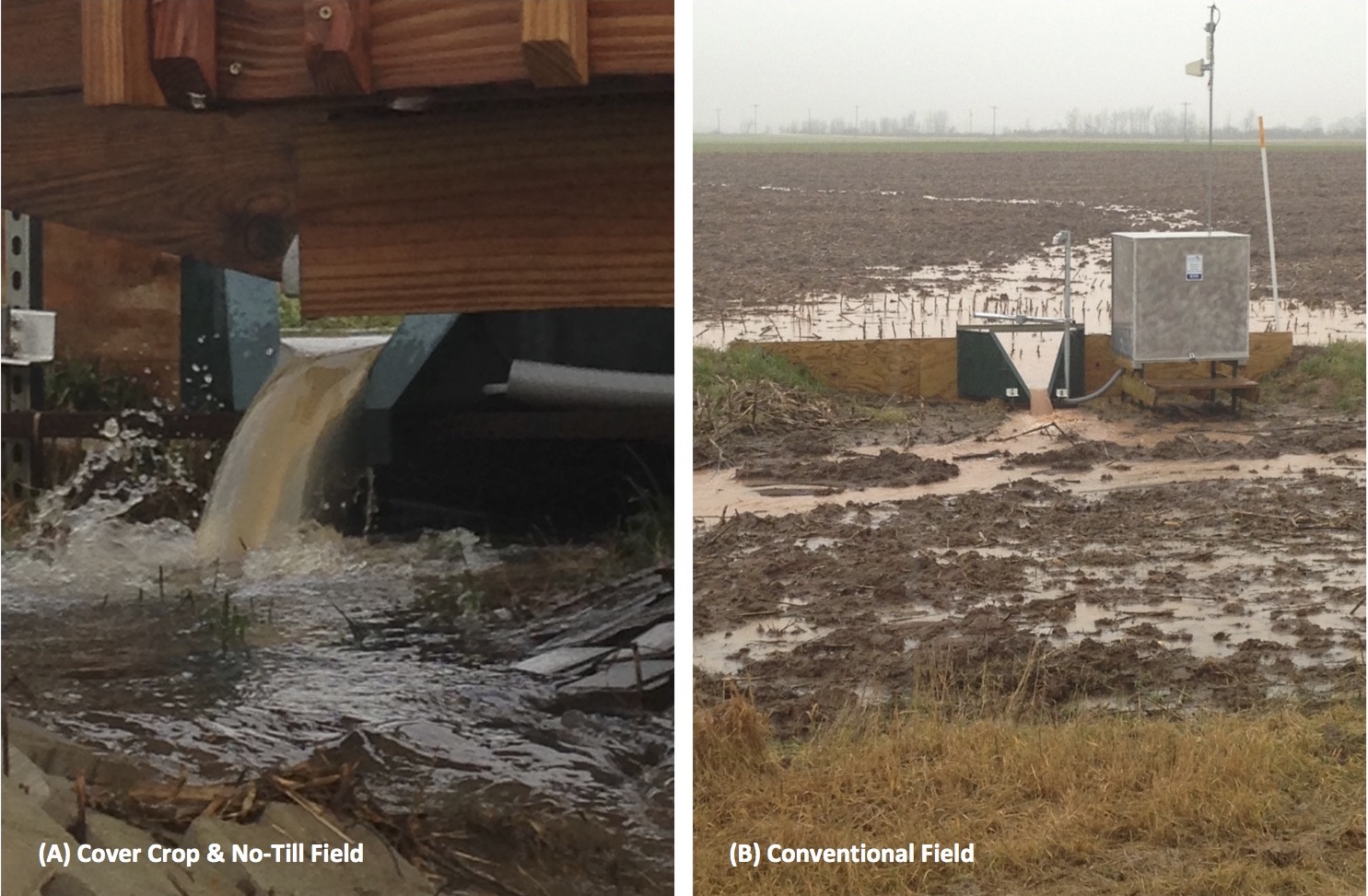

Image 2: Photo credits, Fox Demo Farms. Images illustrate how effective cover crops can be in reducing sediment runoff. Cover crops help retain soil and sediment on the field (A). Conventional tillage practices and no cover crops, result in poor infiltration rates and poor soil structure, which increases sediment runoff (B).
For more information, please visit Cover Crops in Wisconsin!

